An Interesting Finding of C Array Symbols
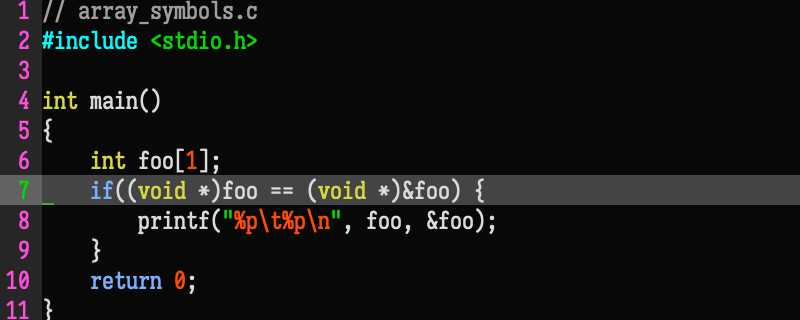
Please check the programming code in C/C++ below:
// array_symbols.c
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int foo[1];
if((void *)foo == (void *)&foo) {
printf("%p\t%p\n", foo, &foo);
}
return 0;
}The output may be like this:
0x16f21afc8 0x16f21afc8The two addresses are the same, which means that in C/C++, array names and addressing array names are equivalent, the array’s name itself acts as a pointer to its first element.